Uncovering the Hidden Threat: Your Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Eliminating Bed Bugs!

Bed Bugs (Cimex lectularius
)
Size: 4–5 mm in length (adult)
Color: Reddish-brown, becoming darker after feeding
Body Shape: Oval, flat, and wingless
Legs: Six, with well-developed legs for crawling
Antennae: Short and segmented, used for sensing vibrations and heat
Mouthparts: Developed for piercing and extracting blood
- Recognized by small, flat bodies and reddish hue
- Active primarily at night when they feed on hosts' blood
Feeding Preferences
Bed bugs primarily feed on the bodily fluids of humans and other warm-blooded creatures, using their specialized mouthparts to pierce the skin and extract a small amount of nourishment. In areas with high population density, they are most active at night, targeting individuals during sleep. They are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by their targets, which allows them to locate hosts even in crowded environments. Urban living spaces, such as shared accommodations, hotels, and apartment complexes, provide ample opportunities for them to access hosts. These pests thrive in close quarters, feeding in small, repeated intervals, and are capable of surviving for weeks without a meal if necessary. Their ability to remain undetected while targeting sleeping individuals has made them a persistent issue in densely populated areas.
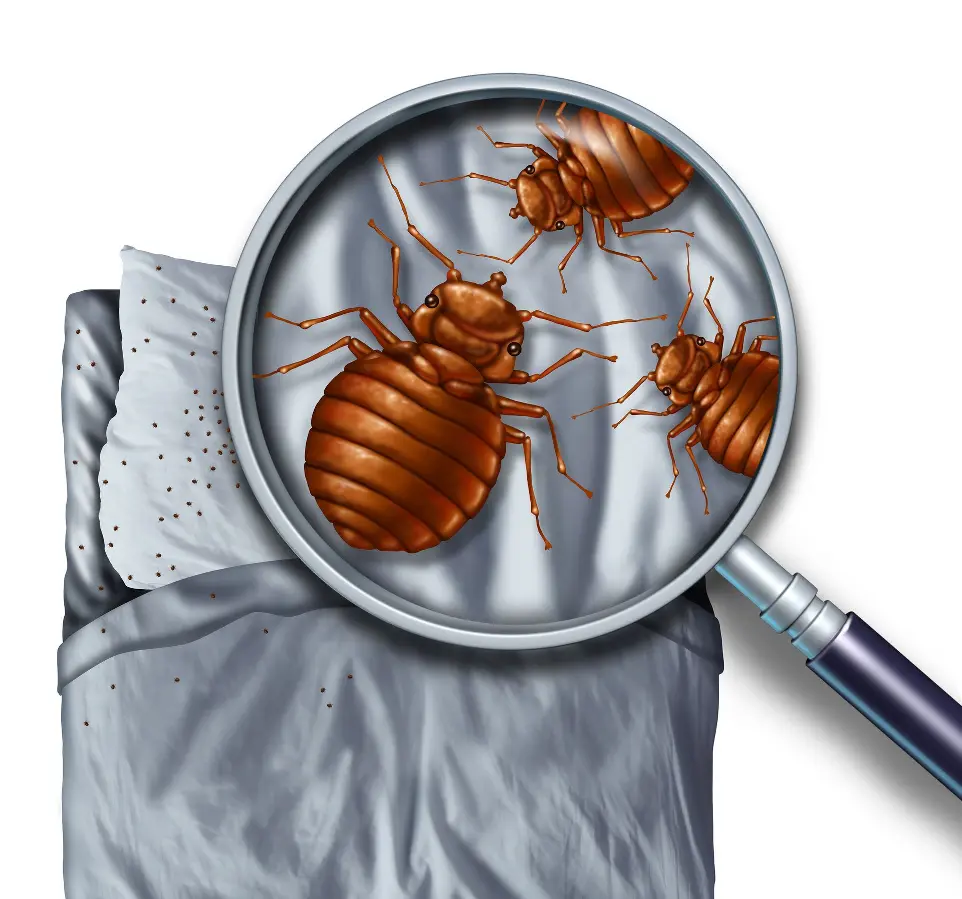

Habitat
Bed bugs are commonly found in places with high human activity and shared living spaces. They thrive in areas with easy access to resting spots, such as upholstered furniture, mattresses, and other soft surfaces close to where people sleep. They are often located in cracks and crevices near walls, furniture joints, and other hidden spaces, allowing them to stay out of sight during the day. In busy areas with apartments, hotels, and multi-unit buildings, they can spread easily due to their ability to hitch rides on personal items or clothing. Their presence is less about cleanliness and more about the availability of shelter and access to nearby food sources.
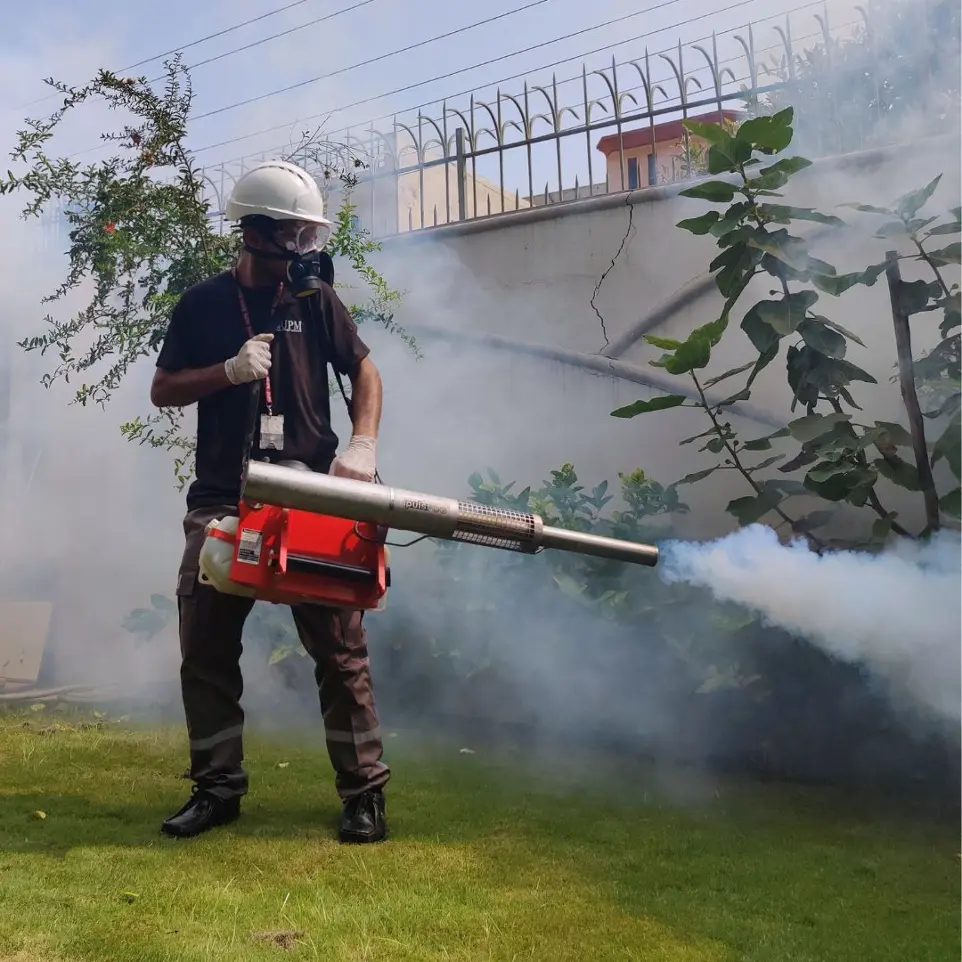

UPM's AIR Approach for Bed Bugs:
- Assess: Inspect your home thoroughly for signs of bed bug activity, such as bites on the skin, blood stains on bedding, dark spots of fecal matter, and shed exoskeletons. Focus on areas around beds, mattresses, and furniture to assess the severity of the infestation.
- Implement: Use targeted treatments such as bed bug sprays, heat treatments, and steam cleaning. Wash and heat-dry bedding and clothing, vacuum frequently, and consider professional pest control services for comprehensive treatment.
- Review: Regularly monitor affected areas for signs of continued activity, and continue preventive measures like using bed bug-proof mattress encasements, sealing cracks, and maintaining cleanliness to prevent future infestations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Look for tiny reddish-brown insects in mattress seams, dark spots on bedding, or small red bite marks on the skin.
They are usually brought in through luggage, used furniture, or clothing from infested areas.
Yes, they can travel through small cracks, shared walls, or personal belongings.
Regularly inspect secondhand furniture, seal gaps in walls, and avoid placing luggage or personal items near shared spaces.
Signs include small bites on skin, blood spots on sheets, or noticing the insects in dark crevices near sleeping areas
No, they require targeted treatments to eliminate them completely.
While some DIY methods may help reduce numbers temporarily, professional treatment is usually necessary for a complete solution.